Aquaponics combines the two systems in a symbiotic environment. It cancels the negative aspects of each. Aquaponics uses highly nutrient effluent from fish that contain virtually all the nutrients needed for optimum growth of plants. Instead of discharging water, Aquaponics uses plants to cleanse and purify the water, after which the water is put back in the aquarium/fish tank/fishpond. This water can be reused but must be topped up at certain stages due to losses from evaporation and plant usage.
 Nitrogen Cycle
Nitrogen Cycle
Bacteria
Bacteria thrive in the dark gravels of culture beds and Breeze elements in the water in a form that plants can absorb and use. An Aquaponics system is organic by nature. Synthetic fertilizers may not be given in food plants without risk of harm to fish and beneficial bacteria, the system must be maintained naturally. There are two different bacteria that break down fish waste, the first is the Nitrosomonas, that convert ammonia to nitrite. These nitrites are then converted to nitrate by Nitrobacter bacteria, plants can then consume nitrates and grow. Figure on the right illustrates the nitrogen cycle.
Mineralisation
However, some accumulation of solids may be bene-ficial. As solids are decomposed by microorganisms, inorganic nutrients essential to plant growth are released to the water, a process known as mineralisation. Mineralisation supplies several essential nutrients. Without sufficient solids for mineralisation, more nutrient supplementation is required, which increases the operating expense and management complexity of the system.
Solids
Most of the fecal waste fish generate should be removed from the waste stream before it enters the hydro-ponic tanks.
Solid Removal Filters
Most of the fecal waste fish generate should be removed from the waste stream before it enters the hydroponic tanks. Other sources of particulate waste are uneaten feed and organisms (e.g., bacteria, fungi and algae) that grow in the system.
If this organic matter accumulates in the system, it will depress dissolved oxygen (DO) levels as it decays and produce carbon dioxide and ammonia.
If deep deposits of sludge form, they will decompose anaerobically (with- out oxygen) and produce methane and hydrogen sulfide, which are very toxic to fish.
Solid Removal Filter Types
Here are some of the common devices used for solid removal from recirculating systems. These include settling basins, tube or plate separators, the combination particle trap and sludge separator, centrifugal separators, micro-screen filters and bead filters. Sedimentation devices (e.g., settling basins, tube, or plate separators) primarily remove settleable solids (>100 microns)
 Swirl Filter
Swirl Filter
This type of Aquaponics filter requires a large barrel shaped container with an inner cylinder basket that filters out solid waste types. It filters out the debris by slowing down the water which causes the heavier particles to descend to the bottom of the container.
The barrel needs to be cleaned out from time to time but be sure to not use soap products when cleaning. This is because the soap chemicals are harmful to the beneficial bacteria. So don’t overdo it when cleaning, you just want to remove the solid wastes, so they don’t clog up the filter. The slime on the sides of the barrel contains a lot of the bacteria that will be helpful to the plants.
Swirl water filters are very popular with most grow bed types. They are available online but for the home aquaponics gardener it can be a DIY project using a barrel with 50–60-gallon capacity (give or take). Commercial systems are going to use filters that require 500-gallon capacity and more.
 Rafter Water Filter
Rafter Water Filter
Another Aquaponics solid removal filter that is efficient at screening out the bigger solids, the Raft water filter, features two chambers or filtration layers. The first chamber captures the larger solid wastes. Next the water overflows into the 2nd chamber where finer particles descend to the bottom and are left behind as the clean water is piped to the grow bed.
This type of filter is very efficient but isn’t commonly used because it can be expensive. It also can take up quite a bit of space.
Crucial to this type of filter is oxygenation of the water. This is facilitated by placing air stones (porous stone) in the filtration device. Then there are the pumps that aerate the water by keeping the flow movement through the pipes from the fish tank into the raft chambers. Monitoring the pumps is essential because if they fail it would be catastrophic for the fish and the plants-they both need constant oxygen.
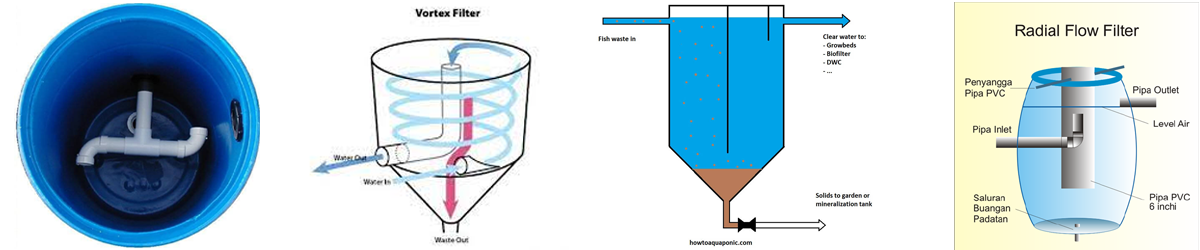
 Radial Flow Filter
Radial Flow Filter
A radial flow Aquaponics filter is like the Swirl filters in that you start with a barrel of approximately 50 gallons capacity. Then a pipe is connected from the fish tank to the barrel extending inward to its middle, then angling 90 degrees upward near the top. This is where the bigger solids are filtered in a way that sends them down to the bottom of the barrel while the nutrient-rich water it piped to the grow bed.
Drum Filter
The drum Aquaponics filter is normally set in a box-like chamber. Inside the filter there are 2 sides, the dirty water side that is piped in from the fish tank, and a clean side that will be piped to the grow bed.
This type of Aquaponics filter requires a large barrel-shaped container with an inner cylinder basket that filters out solid waste types. It filters out the debris by slowing down the water which causes the heavier particles to descend to the bottom of the container.